ggpmisc也是ggplot2的扩展包(或者说是ggplot2生态圈中的一份子),它可以方便的展示诸如直线回归、并添加回归方程、方差分析表等等一些操作,极大的方便了R绘图效率。
# 安装
install.packages("ggpmisc")下面挑选部分经典案例做一个简单介绍:
# 一下示例基于下面R包,如果需要模仿示例运行,请酌情安装
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
library(ggthemes)
library(ggpmisc)
library(ggrepel)
library(xts)
library(lubridate)
library(tibble)
library(nlme)1)时间序列绘图:
# lynx自带演示数据
ggplot(lynx, as.numeric = FALSE) + geom_line() +
stat_peaks(colour = "red") +
stat_peaks(
geom = "text",
colour = "red",
vjust = -0.5,
check_overlap = TRUE
) +
theme_few() +
ylim(-100, 7300)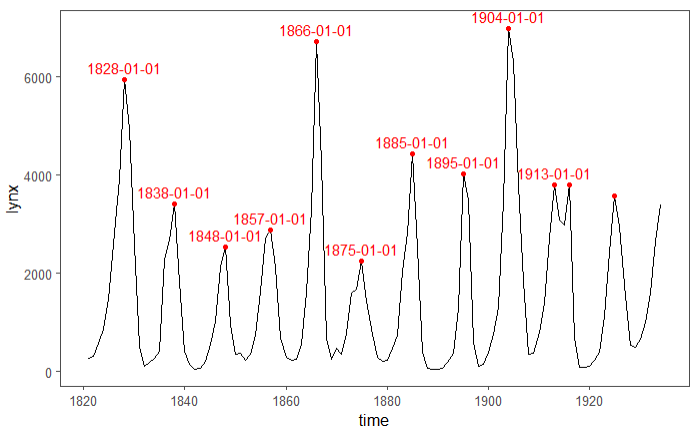
2)象限统计分面图:
set.seed(2020)
# 生成演示数据
x <- -99:100
y <- x + rnorm(length(x), mean = 0, sd = abs(x))
my.data <- data.frame(x,
y,
group = c("A", "B"))
ggplot(my.data, aes(x, y, colour = group)) +
geom_quadrant_lines() +
stat_quadrant_counts(geom = "label_npc") +
geom_point() +
expand_limits(y = c(-260, 260)) +
theme_few() +
facet_wrap( ~ group)
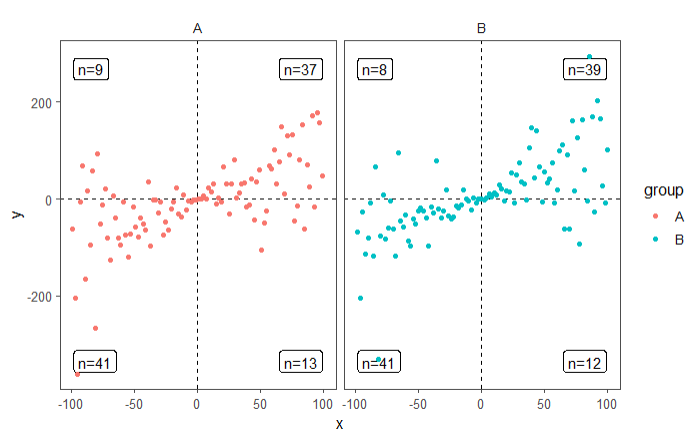
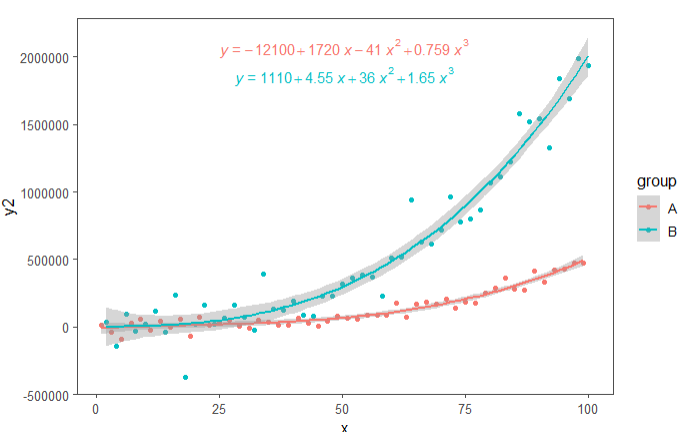
3)回归方程+拟合线
set.seed(2020)
# 演示数据
x <- 1:100
y <-
(x + x ^ 2 + x ^ 3) + rnorm(length(x), mean = 0, sd = mean(x ^ 3) / 4)
my.data <- data.frame(
x,
y,
group = c("A", "B"),
y2 = y * c(0.5, 2),
block = c("a", "a", "b", "b"),
wt = sqrt(x)
)
formula <- y ~ poly(x, 3, raw = TRUE)
ggplot(my.data, aes(x, y2, colour = group)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method = "lm", formula = formula) +
theme_few() +
stat_poly_eq(
aes(label = stat(eq.label)),
formula = formula,
parse = TRUE,
label.x = "centre"
)
set.seed(2020)
# 演示数据
x <- 1:100
y <-
(x + x ^ 2 + x ^ 3) + rnorm(length(x), mean = 0, sd = mean(x ^ 3) / 4)
my.data <- data.frame(
x,
y,
group = c("A", "B"),
y2 = y * c(0.5, 2),
block = c("a", "a", "b", "b"),
wt = sqrt(x)
)
formula <- y ~ poly(x, 3, raw = TRUE)
ggplot(my.data, aes(x, y2, colour = group, fill = block)) +
geom_point(shape = 21, size = 3) +
geom_smooth(method = "lm", formula = formula) +
stat_poly_eq(
aes(label = stat(rr.label)),
size = 3,
alpha = 0.2,
geom = "label_npc",
label.y = c(0.95, 0.85, 0.95, 0.85),
formula = formula,
parse = TRUE
) +
theme_few() +
facet_wrap( ~ group, scales = "free_y")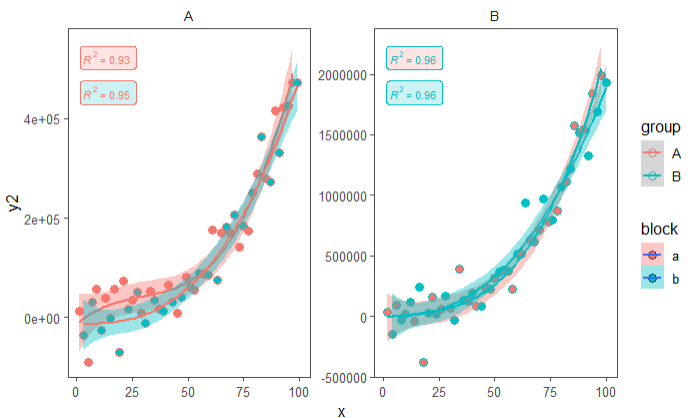
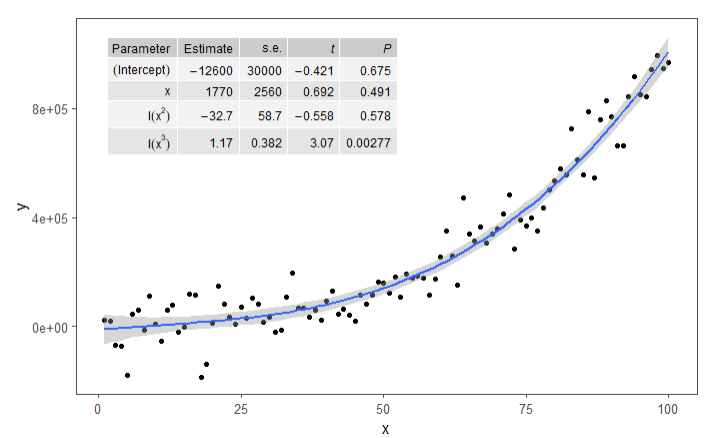
4)添加方差分析表
set.seed(2020)
# 演示数据
x <- 1:100
y <-
(x + x ^ 2 + x ^ 3) + rnorm(length(x), mean = 0, sd = mean(x ^ 3) / 4)
my.data <- data.frame(
x,
y,
group = c("A", "B"),
y2 = y * c(0.5, 2),
block = c("a", "a", "b", "b"),
wt = sqrt(x)
)
formula <- y ~ x + I(x ^ 2) + I(x ^ 3)
ggplot(my.data, aes(x, y)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method = "lm", formula = formula) +
theme_few() +
stat_fit_tb(
method = "lm",
method.args = list(formula = formula),
tb.vars = c(
Parameter = "term",
Estimate = "estimate",
"s.e." = "std.error",
"italic(t)" = "statistic",
"italic(P)" = "p.value"
),
label.y = "top",
label.x = "left",
parse = TRUE
)
5)数据加标注等
random_string <- function(len = 6) {
paste(sample(letters, len, replace = TRUE), collapse = "")
}
# 演示数据
set.seed(2020)
d <- tibble::tibble(
x = rnorm(100),
y = rnorm(100),
group = rep(c("A", "B"), c(50, 50)),
lab = replicate(100, {
random_string()
})
)
ggplot(data = d, aes(x + rep(c(-2, 2), rep(50, 2)),
y, colour = group)) +
theme_few() +
geom_point() +
stat_dens2d_filter(shape = 1,
size = 3,
keep.fraction = 0.25)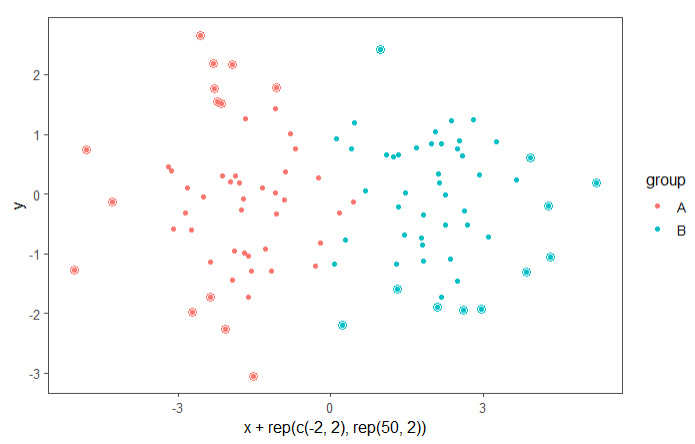
ggplot(data = d, aes(x, y, label = lab, colour = group)) +
geom_point() +
theme_few() +
stat_dens2d_filter(geom = "text_repel", keep.fraction = 0.5)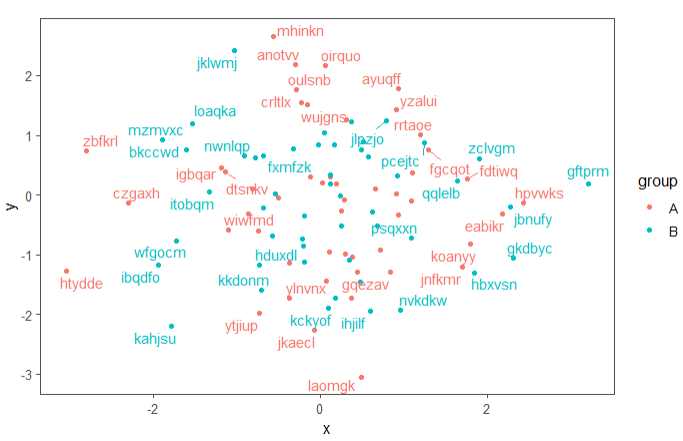
6)还能画火山图
volcano_example.df %>%
mutate(., outcome.fct = outcome2factor(outcome)) %>%
ggplot(., aes(logFC, PValue, colour = outcome.fct)) +
geom_point() +
scale_x_logFC(name = "Transcript abundance%unit") +
scale_y_Pvalue() +
scale_colour_outcome() +
theme_few() +
stat_quadrant_counts(data = . %>% filter(outcome != 0))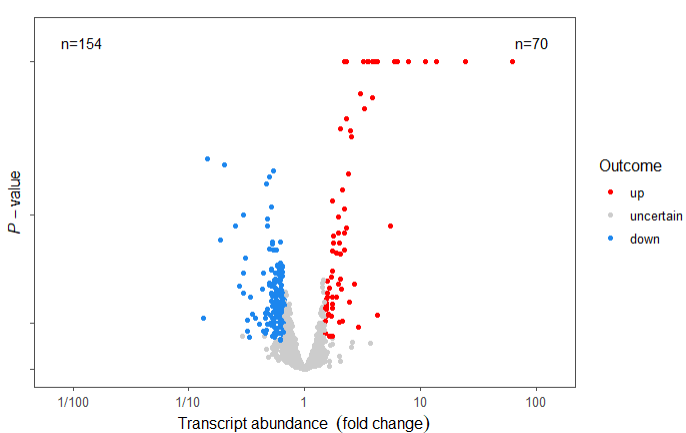
总体感觉此包功能上还是蛮全面的,也做了很多个性化的设置,以上就是此包的主要一些功能介绍本文旨在抛砖引玉,更多详细的内容请大家查看官方文档。
参考资料:
1.https://docs.r4photobiology.info/ggpmisc/index.html

 浙公网安备 33010802011761号
浙公网安备 33010802011761号