TensorFlow™ 是一个采用数据流图(data flow graphs),用于数值计算的开源软件库。节点(Nodes)在图中表示数学操作,图中的线(edges)则表示在节点间相互联系的多维数据数组,即张量(tensor)。它灵活的架构让你可以在多种平台上展开计算,例如台式计算机中的一个或多个CPU(或GPU),服务器,移动设备等等。
其本身入门门槛也相对较高,本次我们常见的随机森林模型演示一次完整的建模和预测过程,数据集我们采用MNIST图象数据,系统环境如下:
python:3.6.8
tensorflow-gpu:1.13.1
from __future__ import print_function
# 是否启用GPU,如果不用GPU此处留空
import os
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "0"
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python.ops import resources
from tensorflow.contrib.tensor_forest.python import tensor_forest
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import pandas as pd随机森林建模:
tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.ERROR)
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("data/", one_hot=False)
# 参数
num_steps = 500 # 训练次数
batch_size = 512 # 每批样本数
num_classes = 10 # 多少个分类0~9,10个
num_features = 784 # 特征数,每张图片是28*28点像素
num_trees = 500 # 随机森林参数,树的个数
max_nodes = 500 # 树的最大节点数
# 输入数据
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, num_features])
# Random forest, 标签必须是整数,(label编号也适用)
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[None])
# Random Forest参数定义
hparams = tensor_forest.ForestHParams(num_classes=num_classes,
num_features=num_features,
num_trees=num_trees,
max_nodes=max_nodes).fill()
# 创建Random Forest
forest_graph = tensor_forest.RandomForestGraphs(hparams)
# 生成图
train_op = forest_graph.training_graph(X, Y)
loss_op = forest_graph.training_loss(X, Y)
# 准确率计算
infer_op, _, _ = forest_graph.inference_graph(X)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(infer_op, 1), tf.cast(Y, tf.int64))
accuracy_op = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
# 初始化变量
init_vars = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(),
resources.initialize_resources(resources.shared_resources()))
# 保存模型
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 运行初始化
sess.run(init_vars)
# 开始训练模型
for i in range(1, num_steps + 1):
# 数据准备
# 获取下一批MNIST数据
batch_x, batch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
_, l = sess.run([train_op, loss_op], feed_dict={X: batch_x, Y: batch_y})
if i % 100 == 0 or i == 1:
acc = sess.run(accuracy_op, feed_dict={X: batch_x, Y: batch_y})
print('Step %i, Loss: %f, Acc: %f' % (i, l, acc))
# 测试模型
test_x, test_y = mnist.test.images, mnist.test.labels
value = pd.DataFrame(sess.run(infer_op, feed_dict={X: test_x}))
value['Label'] = test_y
print("Test Accuracy:", sess.run(accuracy_op, feed_dict={X: test_x, Y: test_y}))
# 将模型保存到磁盘
save_path = saver.save(sess, "model.ckpt")此处我们可以看到value建模效果:
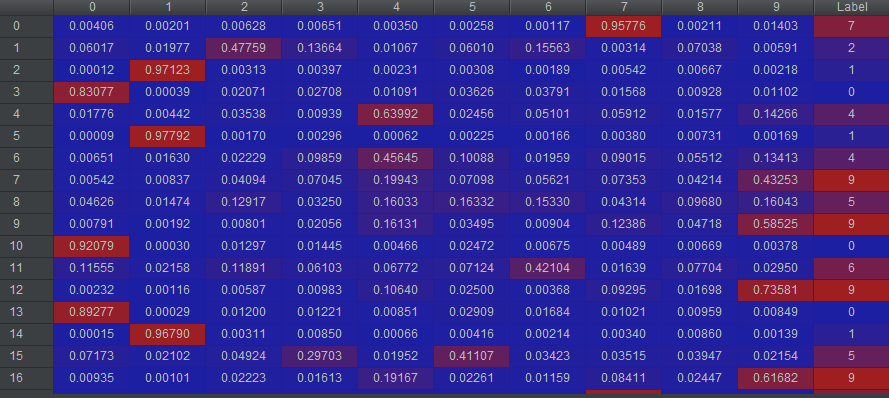
结果是对0~9这10个数字进行概率计算,概率最大的即我们预测结果,总体来说使用起来是非常方便的,计算结果:
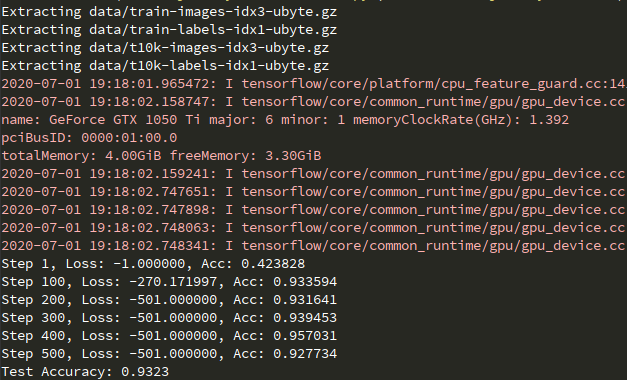
此处我们保存模型为:model.ckpt,下面我们展示如何调用模型会用到。
加载我们训练好的模型:
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("data/", one_hot=False)
# 测试
test_x, test_y = mnist.test.images, mnist.test.labels
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 加载模型 import_meta_graph
saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph("model.ckpt.meta")
# 检查checkpoint
saver.restore(sess, tf.train.latest_checkpoint("./"))
# 获取图
graph = tf.get_default_graph()
X = graph.get_tensor_by_name("Placeholder:0")
Y = graph.get_tensor_by_name("Placeholder_1:0")
# 获取模型
infer_op = graph.get_tensor_by_name('probabilities:0')
value = pd.DataFrame(sess.run(infer_op, feed_dict={X: test_x}))
value['Label'] = test_y
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(infer_op, 1), tf.cast(Y, tf.int64))
accuracy_op = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
print("Test Accuracy:", sess.run(accuracy_op, feed_dict={X: test_x, Y: test_y}))我们用get_tensor_by_name加载模型,由于我们在建模时未指定变量名称,所以此处调用用默认的名称。
如此一个简单的调用完成了,下面是所有代码:
from __future__ import print_function
# 是否启用GPU,如果不用GPU此处留空
import os
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "0"
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python.ops import resources
from tensorflow.contrib.tensor_forest.python import tensor_forest
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import pandas as pd
# Random Forest(随机森林)算法是通过训练多个决策树,生成模型,然后综合利用多个决策树进行分类。
if __name__ == "__main__":
is_Train = True
if is_Train:
tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.ERROR)
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("data/", one_hot=False)
# 参数
num_steps = 500 # 训练次数
batch_size = 512 # 每批样本数
num_classes = 10 # 多少个分类0~9,10个
num_features = 784 # 特征数,每张图片是28*28点像素
num_trees = 500 # 随机森林参数,树的个数
max_nodes = 500 # 树的最大节点数
# 输入数据
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, num_features])
# Random forest, 标签必须是整数,(label编号也适用)
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[None])
# Random Forest参数定义
hparams = tensor_forest.ForestHParams(num_classes=num_classes,
num_features=num_features,
num_trees=num_trees,
max_nodes=max_nodes).fill()
# 创建Random Forest
forest_graph = tensor_forest.RandomForestGraphs(hparams)
# 生成图
train_op = forest_graph.training_graph(X, Y)
loss_op = forest_graph.training_loss(X, Y)
# 准确率计算
infer_op, _, _ = forest_graph.inference_graph(X)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(infer_op, 1), tf.cast(Y, tf.int64))
accuracy_op = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
# 初始化变量
init_vars = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(),
resources.initialize_resources(resources.shared_resources()))
# 保存模型
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 运行初始化
sess.run(init_vars)
# 开始训练模型
for i in range(1, num_steps + 1):
# 数据准备
# 获取下一批MNIST数据
batch_x, batch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
_, l = sess.run([train_op, loss_op], feed_dict={X: batch_x, Y: batch_y})
if i % 100 == 0 or i == 1:
acc = sess.run(accuracy_op, feed_dict={X: batch_x, Y: batch_y})
print('Step %i, Loss: %f, Acc: %f' % (i, l, acc))
# 测试模型
test_x, test_y = mnist.test.images, mnist.test.labels
value = pd.DataFrame(sess.run(infer_op, feed_dict={X: test_x}))
value['Label'] = test_y
print("Test Accuracy:", sess.run(accuracy_op, feed_dict={X: test_x, Y: test_y}))
# 将模型保存到磁盘
save_path = saver.save(sess, "model.ckpt")
else:
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("data/", one_hot=False)
# 测试
test_x, test_y = mnist.test.images, mnist.test.labels
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 加载模型 import_meta_graph
saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph("model.ckpt.meta")
# 检查checkpoint
saver.restore(sess, tf.train.latest_checkpoint("./"))
# 获取图
graph = tf.get_default_graph()
X = graph.get_tensor_by_name("Placeholder:0")
Y = graph.get_tensor_by_name("Placeholder_1:0")
# 获取模型
infer_op = graph.get_tensor_by_name('probabilities:0')
value = pd.DataFrame(sess.run(infer_op, feed_dict={X: test_x}))
value['Label'] = test_y
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(infer_op, 1), tf.cast(Y, tf.int64))
accuracy_op = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
print("Test Accuracy:", sess.run(accuracy_op, feed_dict={X: test_x, Y: test_y}))
参考资料:
1.http://www.tensorfly.cn/
2.https://tensorflow.google.cn/

 浙公网安备 33010802011761号
浙公网安备 33010802011761号