数据归一化(Normalization)是将数据按比例缩放,使之落入一个小的特定区间,如:[0, 1]或 [-1, 1]。主要目的是为了将其转化为无量纲的纯数值,以便于不同单位或量级的指标能够进行比较和加权。
主要方法有Min-Max Normalization:(X – min(X)) / (max(X) – min(X)
在R中可以用以下代码计算
min_max_norm <- function(x) {
(x - min(x)) / (max(x) - min(x))
}数据标准化(Standardization)数据的标准化是将数据按比例缩放,使之落入一个特定区间。
主要方法有Z-Score Normalization:(X – μ) / σ
在R中可以用以下代码计算
scale(X)
# scale(x, center = TRUE, scale = TRUE) 结果即z-score标准化结果,默认进行均值为0,标准差为1的标准化操作
# center为真表示数据中心化(只减去均值不做其他处理)
# scale为真表示数据标准化如果直接看,会发现两者在概念上有些相似之处,下面比较下两者的区别(直接引用参考资料中的原汁原味表格):
| NO. | Normalisation | Standardisation |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Minimum and maximum value of features are used for scaling | Mean and standard deviation is used for scaling. |
| 2. | It is used when features are of different scales. | It is used when we want to ensure zero mean and unit standard deviation. |
| 3. | Scales values between [0, 1] or [-1, 1]. | It is not bounded to a certain range. |
| 4. | It is really affected by outliers. | It is much less affected by outliers. |
| 5. | Scikit-Learn provides a transformer called MinMaxScaler for Normalization. | Scikit-Learn provides a transformer called StandardScaler for standardization. |
| 6. | This transformation squishes the n-dimensional data into an n-dimensional unit hypercube. | It translates the data to the mean vector of original data to the origin and squishes or expands. |
| 7. | It is useful when we don’t know about the distribution | It is useful when the feature distribution is Normal or Gaussian. |
| 8. | It is a often called as Scaling Normalization | It is a often called as Z-Score Normalization. |
同时建议我们在数据处理、建模的过程中也进行数据的预处理提升数据分析效率及准确性。
参考资料:
1. https://www.statology.org/how-to-normalize-data-in-r/
2.https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/normalization-vs-standardization/
3.https://www.cnblogs.com/ooon/p/4947347.html
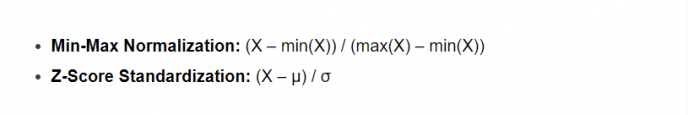
 浙公网安备 33010802011761号
浙公网安备 33010802011761号